 "
"updated April 2024
We start with a data file collab_data_2024_cleaned.csv that was created from within the R markdown file chisq-inclass2024.Rmd.
 "
"
race_ethn_reported, income_or_ses_reported, and location_reported are categorical/nominal variables, each with two levels (0=no,1=yes)
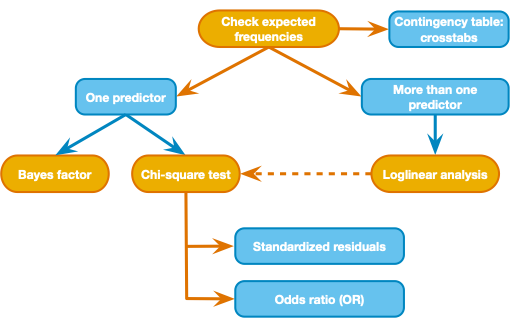
race_ethn_reported, income_or_ses_reported, and location_reported are related, using Analyze, Log Linear, Model Selectionrace_ethn_reported in rowsincome_or_ses_reported in columnslocation_reported in layers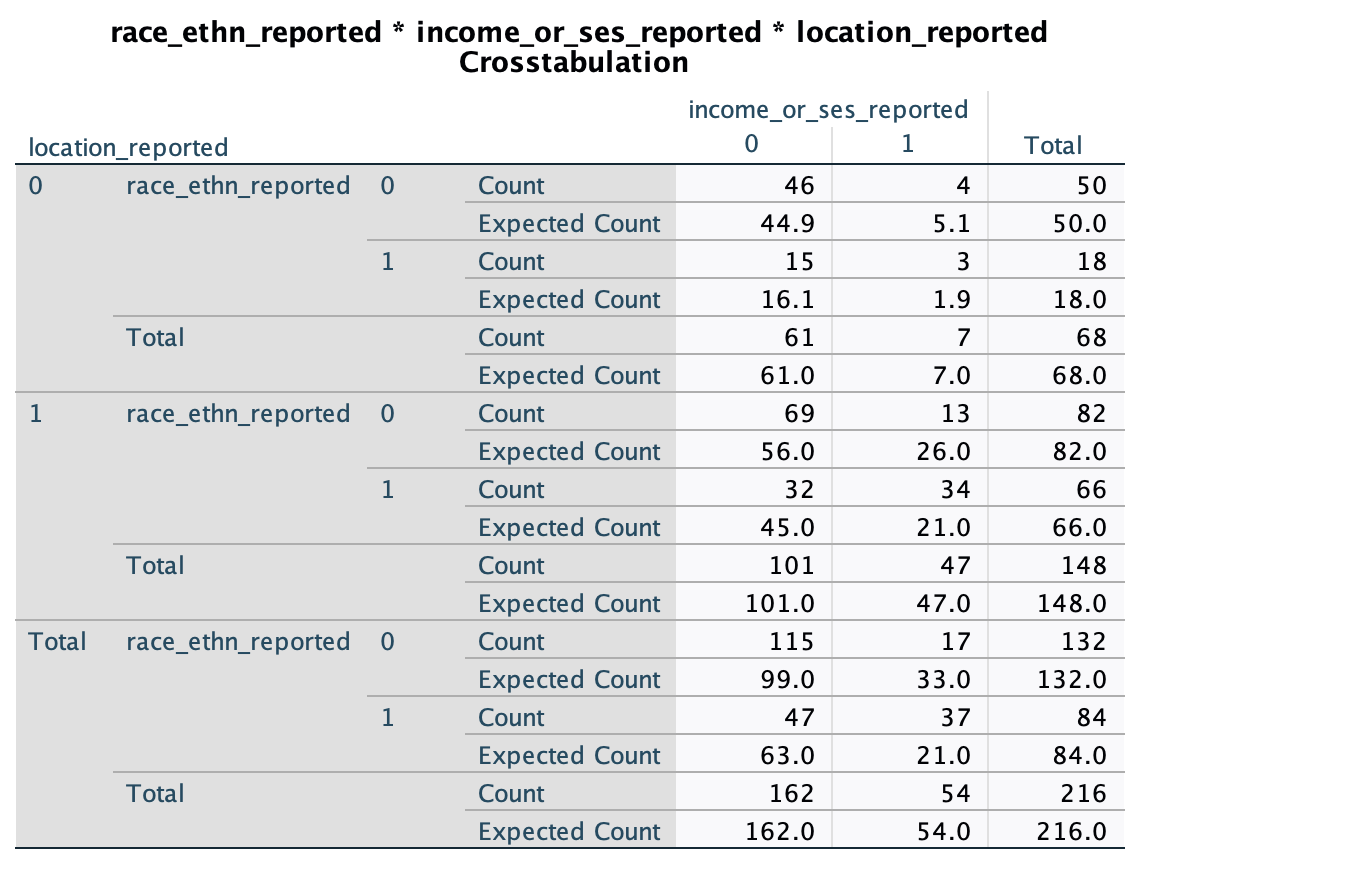
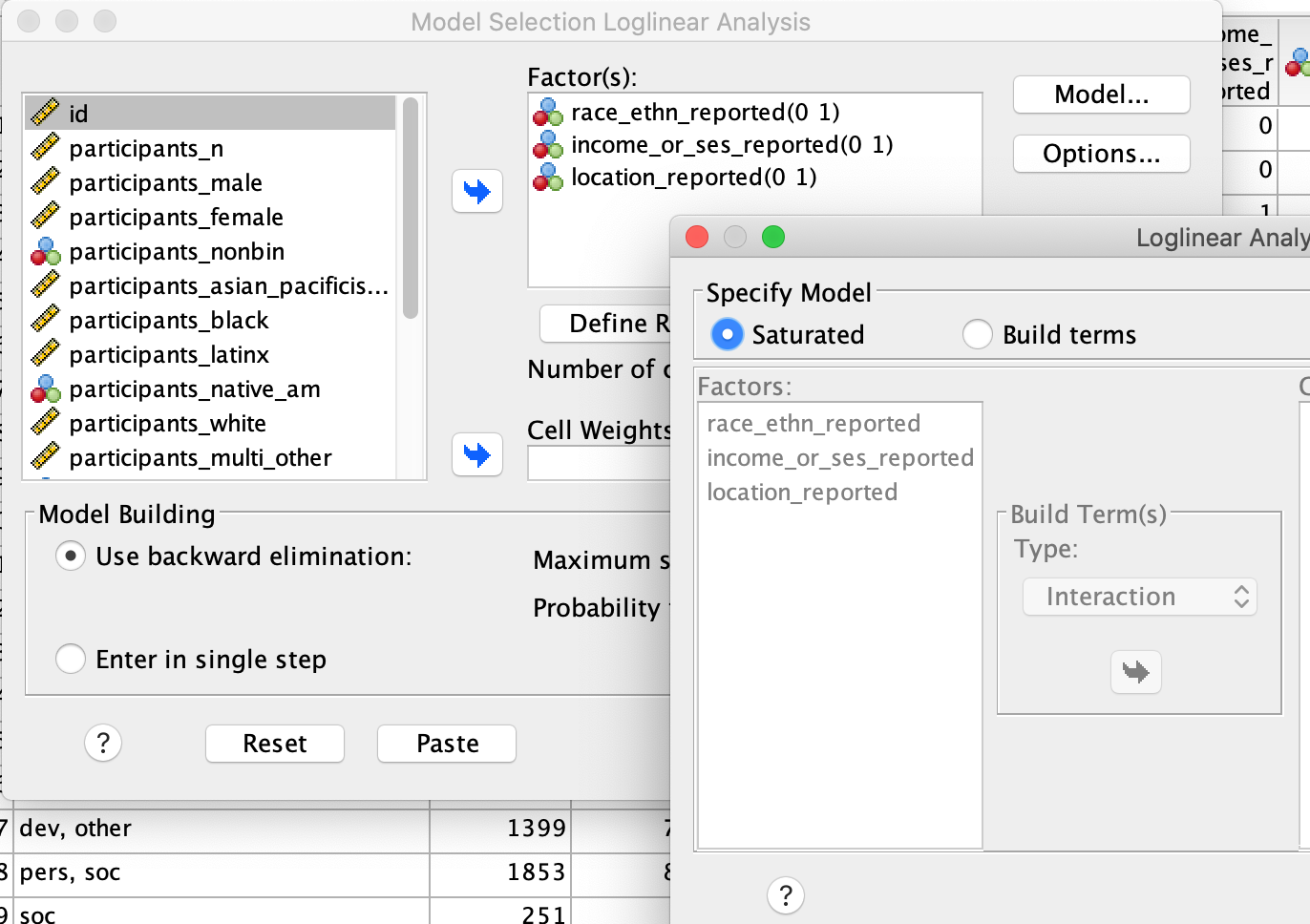
Enter the 3 variables into the "Factors" box, and use the "Define Range" button to define the range for each (minimum=0, maximum=1)
Look for the "Backward Elimination Statistics" table (screenshot below)
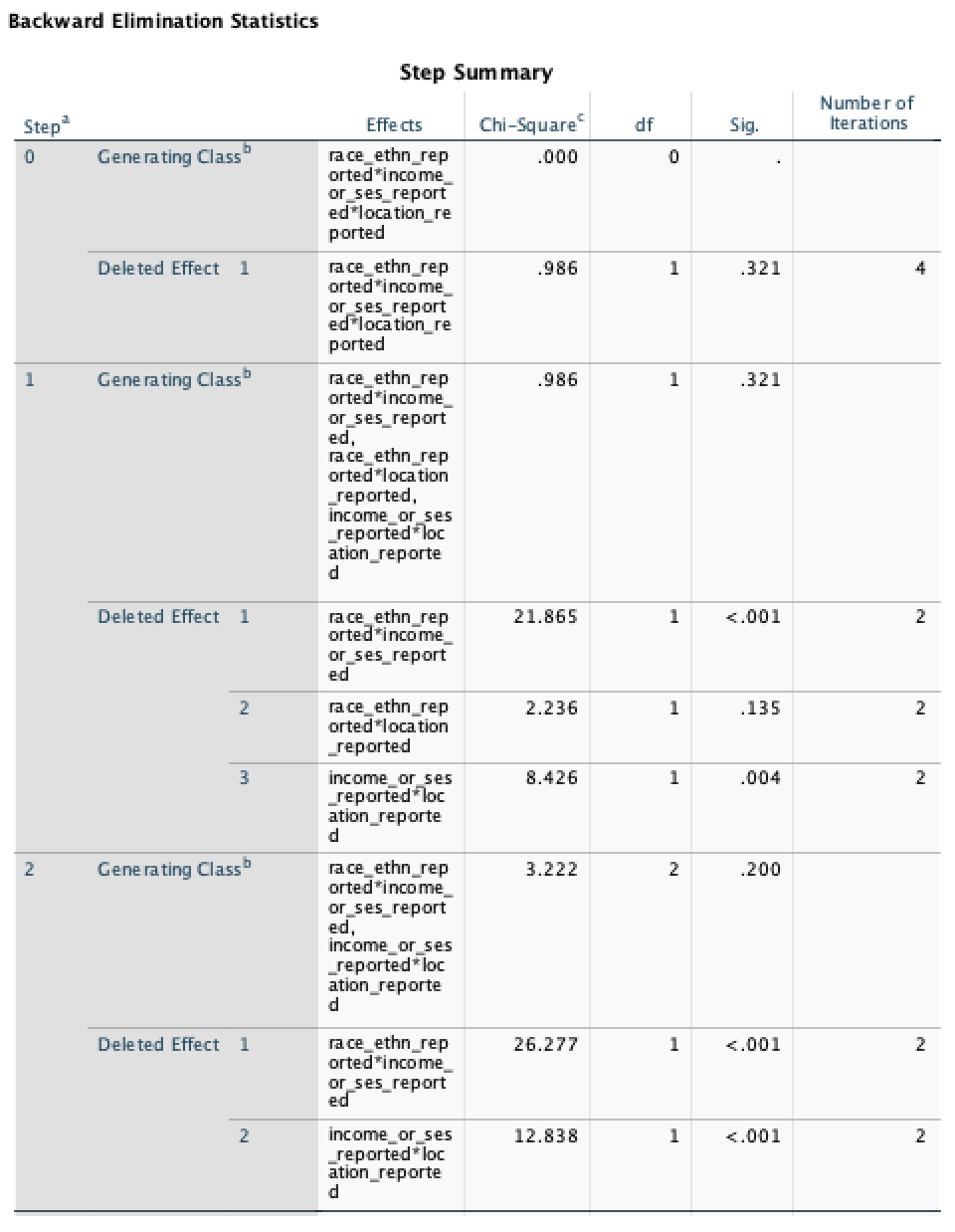
Notice the following:
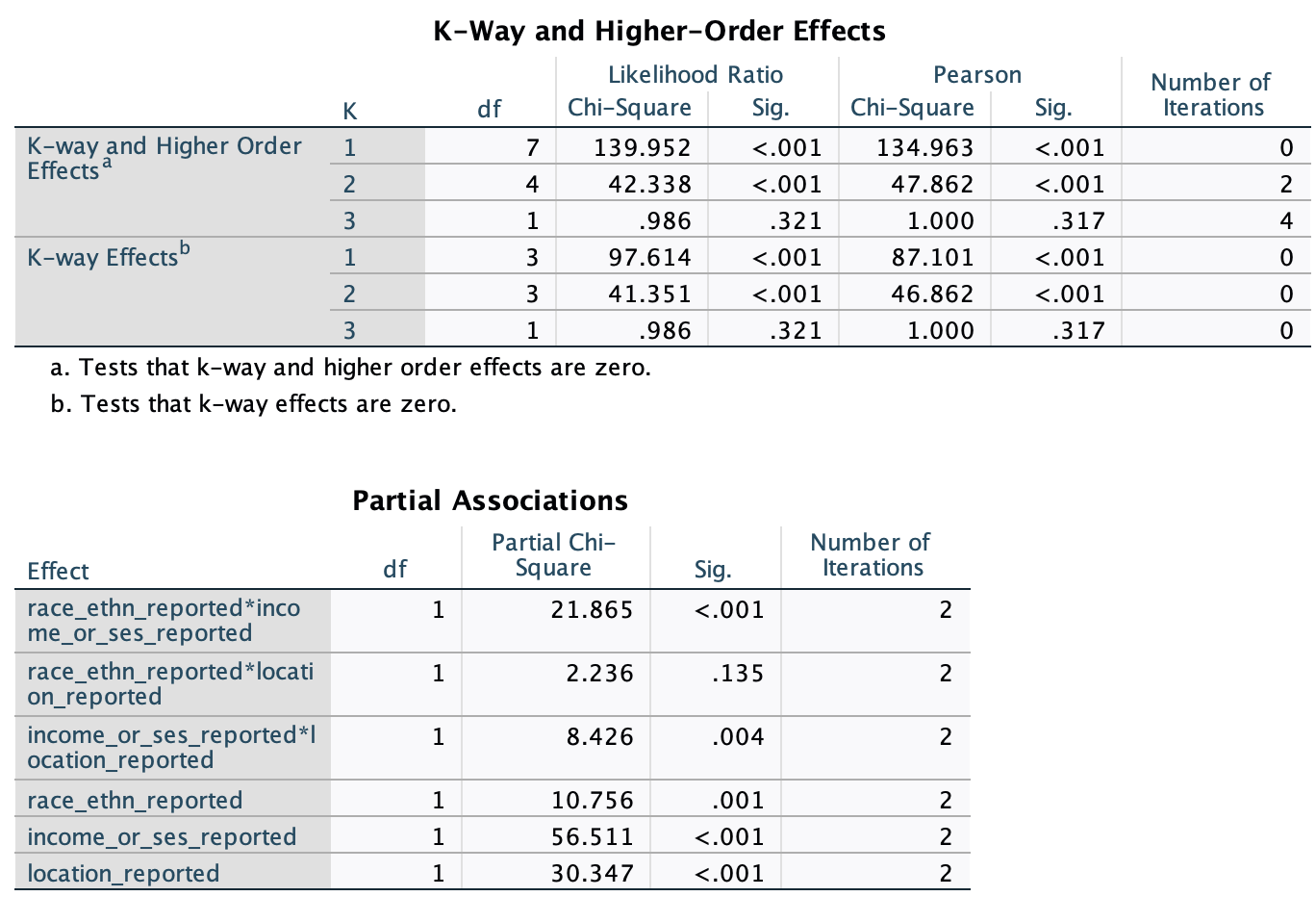
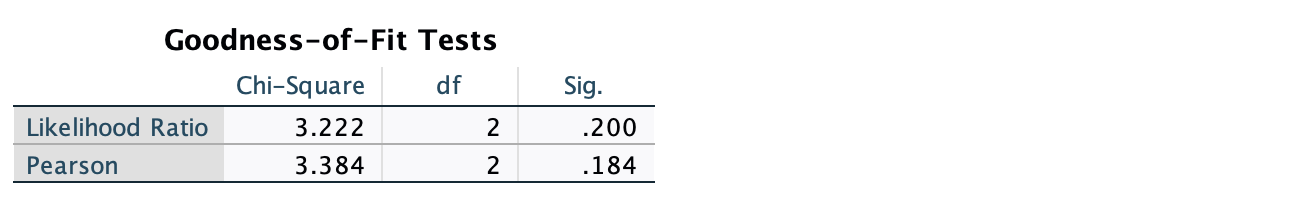
We generate 2-way contingency tables to understand the two-way associations. Expected freqencies in these tables are what we would expect under the null hypothesis (whereas expected freqencies in the loglinear analysis "Cell counts and Residuals" table - not included here - are expected frequencies predicted by the final model). Select the Chi-square and Risk Estimate options under "Statistics" to get the chi-square stat and odds ratios for these associations (included in the reporting section below)
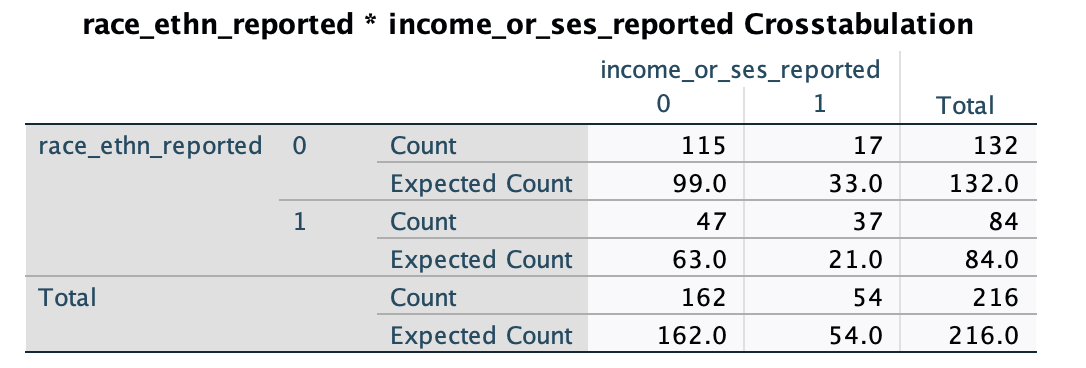
Race reporting*Income reporting: we can see in the table that race is reported more than expected (under the null hypothesis) when income is reported (observed N=37, expected N = 21) and less when income is not reported (observed N=47, expected N = 63).
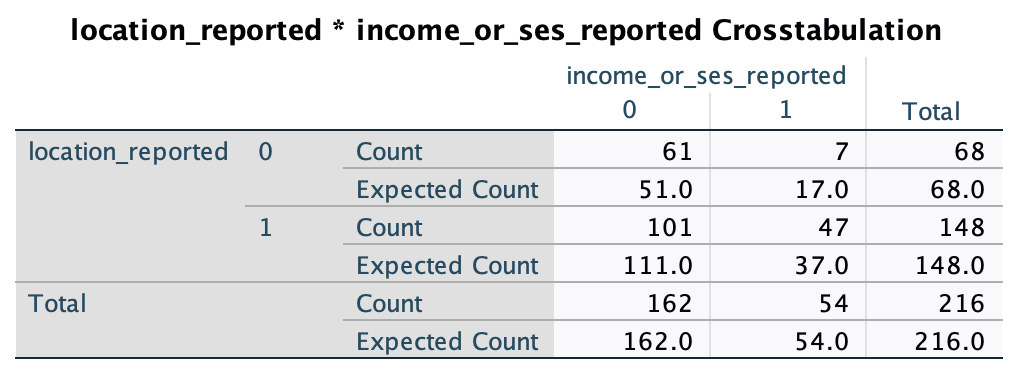
Income reporting*Location reporting: we can see in the table that income/ses is reported more than expected (under the null hypothesis) when location is reported (observed N=47, expected N = 37) and less when income is not reported (observed N=101, expected N = 111).
For this example we could report:
The three-way loglinear analysis produced a final model that retained interactions of (a) race reporting by income/ses reporting and (b) location reporting by income/ses reporting. The likelihood ratio of this final model was χ2(2) = 3.222, p = .200, indicating the model did not significantly differ from the observed frequencies. The highest-order interaction (race reporting by income/ses reporting by location reporting) was not significant, (comparison of model without the three-way interaction to the full model: χ2(1) = 0.986, p = .320), and the race/ethnicity-reported by location-reported interaction was not significant (model without this term compared to model with all 2nd-order interactions: χ2(1) = 2.236, p = .135). To understand the two-ways associations, separate chi-square tests were performed to examine (a) race/ethnicity reporting by income/ses reporting (combining location reporting categories) and (b) location reporting by income/ses reporting (combining race/ethnicity reporting categories). There was a significant association between race/ethnicity-reported and whether location was reported, χ2(1) = 24.961, p < .0001, odds ratio = 5.325. Furthermore, there was a significant association between income/ses-reported and whether location was reported, χ2(1) = 11.447, p = .001, odds ratio = 4.055. [plots/contingency tables can be used to characterize the two-way associations completely]
That's all for today!!!